Monday, Tuesday:
Review Friday's test - any questions?
Remember that the Machine Learning paper is due on Friday, January 8th, at 7:30 AM. Also remember that it was assigned over a month ago! Make yours one that you can be proud of. This might provide some inspiration. (13:56)
Overview of computer history:
Early Computing: Crash Course Computer Science #1 (11:52) Overview of computing up until the early 1900s
The greatest machine that never was (12:14) Babbage, Lovelace, and Turing
Charles Babbage and his Difference Engine #2 (5:47) shows the Difference Engine #2 in action
Electronic Computing: Crash Course Computer Science #2 (10:43) From about 1900 to the beginning of the transistor era
ENIAC (0:38)
SAGE (just watch up to 6:55, the stuff after that is fairly irrelevant)
Recommended, but we won't have enough class time:
The Queen of Code (16:30) Grace Hopper was a serious badass.
Charles Babbage and his Difference Engine #2 (5:47) shows the Difference Engine #2 in action
Electronic Computing: Crash Course Computer Science #2 (10:43) From about 1900 to the beginning of the transistor era
ENIAC (0:38)
SAGE (just watch up to 6:55, the stuff after that is fairly irrelevant)
Recommended, but we won't have enough class time:
The Queen of Code (16:30) Grace Hopper was a serious badass.
How Computers Work:
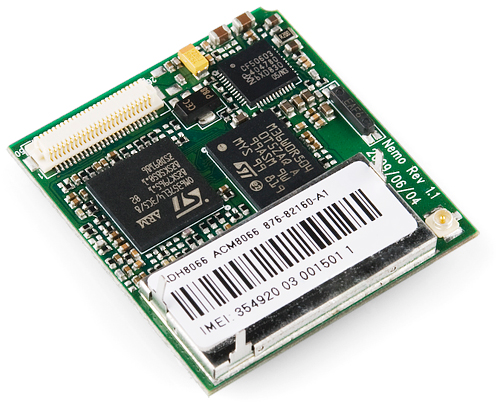
Now we've learned a little about the early days of computing, from the abacus and Charles Babbage's analytical engine to the WW2 era Mark-I and ENIAC, and the gigantic SAGE computers built using vacuum tubes. How do you get from that to a smartphone in your pocket? The answer is the transistor, and the integrated circuit that combines millions or billions of transistors into a smallish chip. Here is a circuit board that has several chips on it -- those black square things:
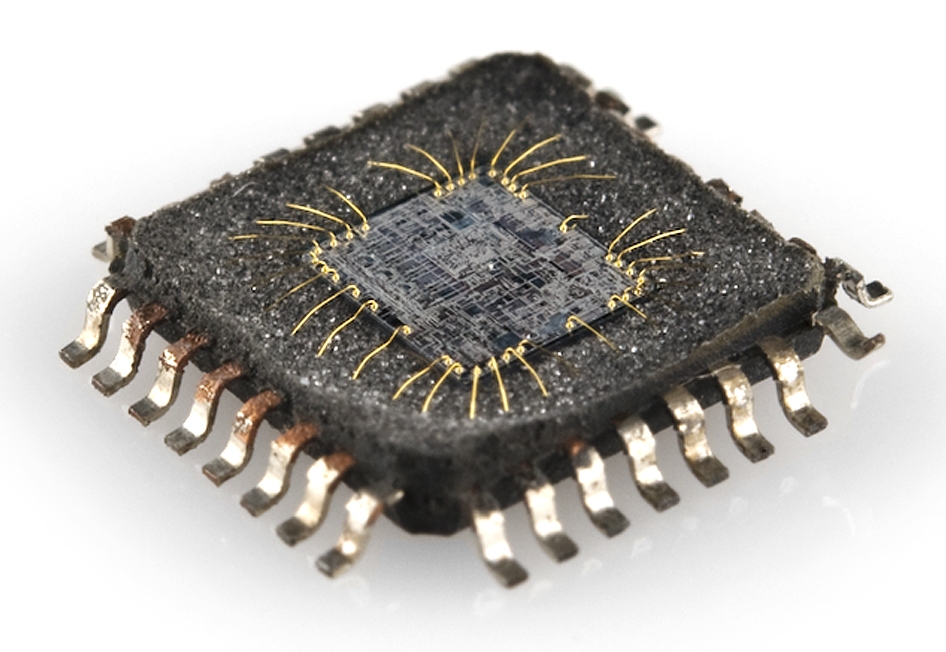
(These images are from sparkfun.com . . . ) Grind the top off one of those chips and it looks like this:
So, how do you make something like this? It's built up in many layers using a very complex technique called photolithograpy. This gives a pretty good picture:
Integrated Circuits and Moore's Law: Crash Course in Computer Science (12:40 + promo at the end)
How do they make silicon wafers and computer chips? (8:53)
50 Years of Moore's Law (2:03)
Zoom into a microchip (3:40)
So, how does all this actually work? Let me try to explain . . .
Here is a copy of the slides I'll be going through (updated).
Demo the Visible Computer.
(These images are from sparkfun.com . . . ) Grind the top off one of those chips and it looks like this:
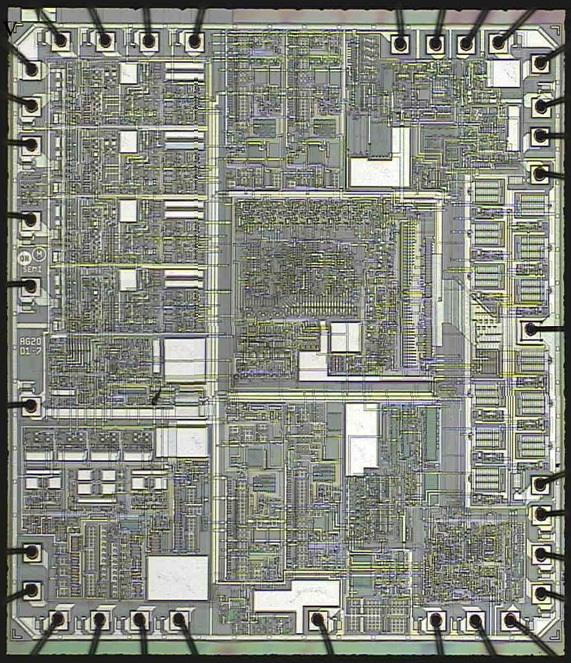
Take a closer look at the little square in the middle with the tiny wires:
Zoom in:
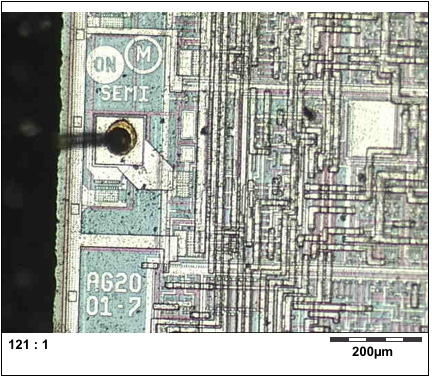
Zoom in more with an electron microscope (not the same chip as above):
So, how do you make something like this? It's built up in many layers using a very complex technique called photolithograpy. This gives a pretty good picture:
Integrated Circuits and Moore's Law: Crash Course in Computer Science (12:40 + promo at the end)
How do they make silicon wafers and computer chips? (8:53)
50 Years of Moore's Law (2:03)
Zoom into a microchip (3:40)
So, how does all this actually work? Let me try to explain . . .
Here is a copy of the slides I'll be going through (updated).
Demo the Visible Computer.
Wednesday:
Wellness day!